Radiobiological Modelling
Group leader: Dr. Thomas Friedrich
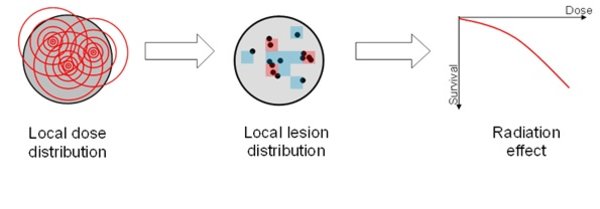
The GSI Radiobiological Modeling Group focuses on the development, validation and application of biophysical models to explain radiation effects to cells or tissues. With mechanistic analytical models we mostly investigate the effects of ion radiation, which show a large effectiveness due to the tremendous energy deposition pattern along their way through cells or tissue, but also other radiation qualities (photons, neutrons) are considered based on their physical properties. The developed models find applications in radiation biology, radiation therapy and radiation protection. Described endpoints range from DNA damage induction over cell survival up to immunogenic or carcinogenic potential. This includes effect predictions for radioimmunotherapy and spatial fractionated radiotherapy
Main research topics
Collaborations
Center for Energy Research, Budapest, Hungary (Balazs Madas)
Mayo Clinic Florida (Keith Furutani)
MIT Marburg / TUM Gießen (Klemens Zink)
PTC Prague, Czech Republic (Sarah Al Hamami)
HIT / DKFZ Heidelberg (Christian Karger, Oliver Jäkel)
Oncoray Dresden (Felix Horst)
Universität der Bundeswehr, München (Günther Dollinger / Judith Reindl)
Raysearch Ltd., Sweden (Industry Collaboration)
PIDE Project
Selected Publications
Friedrich T, Pfuhl T, Scholz M. Spectral composition of secondary electrons based on the Kiefer–Straaten ion track structure model. Physics in Medicine and Biology 69:025013 (2024). doi:10.1088/1361-6560/ad1765
Hufnagl A, Johansson G, Siegbahn A, Durante M, Friedrich T, Scholz M. Modeling secondary cancer risk ratios for proton versus carbon ion beam therapy: A comparative study based on the local effect model. Medical Physics 49:5589-5603 (2022). doi:10.1002/mp.15805
Friedrich T, Pfuhl T, Scholz M. Update of the particle irradiation data ensemble (PIDE) for cell survival. Journal of Radiation Research 62:645-655 (2021). doi:10.1093/jrr/rrab034
Friedrich T, Scholz M, Durante M. A Predictive Biophysical Model of the Combined Action of Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy of Cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 113:872-884 (2022). doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.03.030
Herr L, Friedrich T, Durante M, Scholz M. A model of photon cell killing based on the spatio-temporal clustering of DNA damage in higher order chromatin structures. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e83923. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0083923
Friedrich T, Ilicic K, Greubel C, et al. DNA damage interactions on both nanometer and micrometer scale determine overall cellular damage. Scientific Reports 8:1-10 (2018). doi:10.1038/s41598-018-34323-9
Grün R, Friedrich T, Traneus E, Scholz M. Is the dose-averaged LET a reliable predictor for the relative biological effectiveness? Medical Physics 46:1064-1074 (2019). doi:10.1002/mp.13347
Stewart RD, Carlson DJ, Butkus MP, Hawkins R, Friedrich T, Scholz M. A comparison of mechanism-inspired models for particle relative biological effectiveness (RBE). Medical Physics 45:e925-e952 (2018). doi:10.1002/mp.13207
Mirsch J, Tommasino F, Frohns A, et al. Direct measurement of the 3-dimensional DNA lesion distribution induced by energetic charged particles in a mouse model tissue. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 112:12396-12401 (2015). doi:10.1073/pnas.1508702112
Steinsträter O, Grün R, Scholz U, Friedrich T, Durante M, Scholz M. Mapping of RBE-Weighted Doses Between HIMAC– and LEM–Based Treatment Planning Systems for Carbon Ion Therapy. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 84:854-860 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.01.038
Friedrich T, Scholz U, Elsässer T, Durante M, Scholz M. Calculation of the biological effects of ion beams based on the microscopic spatial damage distribution pattern. International Journal of Radiation Biology 88:103-107 (2011). doi:10.3109/09553002.2011.611213
Elsässer T, Weyrather WK, Friedrich T, et al. Quantification of the relative biological effectiveness for ion beam radiotherapy: direct experimental comparison of proton and carbon ion beams and a novel approach for treatment planning. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 78:1177-1183 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.05.014
Scholz M, Kellerer AM, Kraft-Weyrather W, Kraft G. Computation of cell survival in heavy ion beams for therapy. The model and its approximation. Radiation and Environmental Biophysics 36:59-66 (1997). doi:10.1007/s004110050055
Group Members
Group Leader:
Dr. Thomas Friedrich
Ph.D. Students:
Virginia Boretti
Bachelor Students:
Youness Bouzalmat
Thilo Elsässer
Uwe Scholz
Olaf Steinsträter
Adrian Seeger
Rebecca Grün
Francesco Tommasino
Jona Renner
Tamara Buch
Izabella Zarahdnik
Paul Günther
Lisa Herr
Sylvie Lerchl
Alexander Bothe
Antonia Hufnagl
Tabea Pfuhl
Stefanie Mrozinski
Andreas Brilka
Vincent Pruy
Michael Scholz
Kaya Hilt
Inga Königstein