Open Science GSI/FAIR
For questions, comments, and support please contact open-science(at)gsi.de
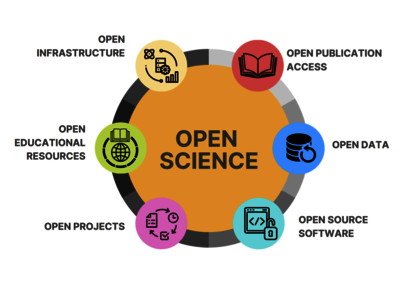
What is Open Science?
Open Science is the practice of making scientific research output openly available in the form of data, software, publications, hardware and infrastructure. This promotes transparency, collaboration, and reproducibility in research, as well as wider access to knowledge for the public and to researchers.
GSI and FAIR are committed to Open Science practices and provide tools, support, and information to internal and external researchers involved in GSI/FAIR projects. Organisations such as UNESCO, the DFG, the BMBF and Helmholtz among many others have recognized the benefits of Open Science, and have issued recommendations to support the movement.
The GSI/FAIR Open Science Working Group hosts monthly meetings to promote and advance Open Science at within the facilities. Membership of this group comprises researchers from a variety of disciplines, as well as members from the accelerator division, Grant Office, Technology Transfer, IT, and Library and Documentation.
Adopting Open Science principles aligns with good scientific practice, and more information on this can be found on the GSI/FAIR Ethics and Rules webpage
The GSI policy on Research Data Management can be found here.
GSI/FAIR Guidelines on Research data management can be found here (2023).
The GSI guidelines on Software licences can be found here (Internal only).
What is Open Access?
GSI/FAIR is committed to providing comprehensive access to scientific knowledge, which is why the scientific management of GSI/FAIR strongly supports the expansion of Open Access of research articles and other academic outputs. Open access categories can be explain using a colour naming system.
- Diamond OA: The journal publishes the article and makes it available to all with no fees involved for either author or reader.
- Gold OA: The publisher makes articles immediately free and available for access for all. Licensing typically is given under creative commons (CC-BY 4.0). There is an article processing charge for this method of publication and the whole journal is open access.
- Hybrid-Gold OA: The publisher makes articles immediately free and available for access for all. Licensing is typically given under creative commons (CC-BY). There is an article processing charge for this method of publication and the journal is not fully open access.
- Green OA: The article is published in a journal but in addition the author may publish the article on a website(s) controlled by the author or institution that funded the work. This may be done after peer review, but before copyediting and typesetting.
For GSI internal persons: to receive publication funding from the GSI Research Division please see (internal only).
For further information on this subject, please contact the Library Department gsilibrary(at)gsi.de .
or in case of third party funding e.g. EU/DFG contact the GSI Grant Office.
What is Open Data?
Open Data refers to the practice of publishing research data in a way that makes it available for anyone to access, use and share. This can be in compliance with theFindable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable principles.
By adhering to the Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable (FAIR) principles, data is made discoverable, accessible and interoperable, promoting transparency, collaboration and reproducibility in research.
This not only benefits researchers but also the general public by enabling their participation in citizen science through the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, ultimately leading to more diverse perspectives, more data and more discoveries.
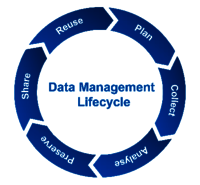
This requires good scientific practice and management and thus falls under the category of Research Data Management (RDM).
RDM involves a life-cycle approach to managing data, including planning, collection, analysis, preservation, sharing, and reuse. By following this cycle, data can be made openly available and reusable.
Data Management Planning
A Data Management Plan (DMP) outlines how data are to be handled both during a research project and after the project is completed. This includes how research data will be collected, processed, stored, and shared during and after a research project. It is strongly advised to prepare a DMP before the start of a research project.
GSI/FAIR offers the software RDMO (Research Data Management Organiser) for the preparation of DMPs.
This tool simplifies the process of preparing and updating DMPs within a project.
Within the software, catalogues for GSI/FAIR projects, as well as for Horizon Europe projects can be found.
Instructions on use can be found here.
Data Publication
GSI/FAIR actively promotes the publishing of research data whenever possible within the bounds of legal, ethical, and technology transfer mandates. The data may also be subject to appropriate embargo periods. Data should be published with a persistent identifier, such as a Digital Object Identifier (DOI) in suitable repositories.For licencing, CC-BY-4.0 is advised.
The handling of research data should, as best as possible, conform to the Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable (F.A.I.R-principles) for scientific data management and stewardship. These principles act as an internationally recognised standard for the publishing of research data. See here for the guidelines, and a summary of the points here: GO-FAIR FAIR Principles.
The Helmholtz Program Oriented Funding IV (POF IV) now requires published research data, as well software and journal articles to be counted for each Helmholtz centre as quality indicators. Thus, GSI/FAIR has recently implemented a strategy and is taking necessary actions to ensure compliance with this requirement.
For instructions on the publication of research data (and research software) at GSI/FAIR please refer to this link.
The Research Data Management Team can be contacted for questions, comments, support and advice: open-science(at)gsi.de
The GSI/FAIR Policy on Research Data Management can be found here (2023).
GSI/FAIR Guidelines on Research data management can be found here (2023).
What is Open Software?
Open software, also known as Free and Open Source Software (FOSS), refers to software that can be used, modified, and distributed without any legal or technical restrictions. It is made available on trusted platforms, allowing anyone to access, reuse, and modify it for any purpose.
GSI/FAIR commits to open source software principles that ensure that the software produced in our laboratory is made available in a way that respects the freedoms of users, and takes into account any potential commercial or third-party use. Software published should be assigned a persistent identifier such as a Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
As with research data, there are a set of guidelines: the FAIR Principles for research software, which can be found here.
GSI/FAIR open software licences are documented here .
For a guide on how to publish software at GSI, please refer to this link.
GSI/FAIR is a collaborating member of the Open-source Scientific Software and Service Repository (OSSR), which is an open-access repository for software collaborative development, uptake and reuse, developed within the ESCAPE project. The OSSR is intended for scientific researchers to share and find software and services. For more information on including software here, please contact open-science(at)gsi.de
Further information on the OSSR can be found here.
Public Money? Public Code!
GSI and FAIR adhere to the FAIR principles, which represent a commitment to responsible and efficient scientific research. Supporting the "Public Money? Public Code!" campaign demonstrates our dedication to transparency, collaboration, innovation, sustainability, and efficiency. The open nature of the software allows for global scrutiny and contributions, resulting in refined, efficient, and sustainable development. Dissemination before monetization is a core principle, aiming for positive impact rather than quick profits. Embracing open models enhances services, reputation, public support, funding, and fosters innovation.
Open software enables global scrutiny and contributions, leading to refined, efficient, and sustainable development. It reflects our commitment to excellence, meeting the high demands of critical infrastructure, physics experiments, and accelerator controls. Learn more.
It is strongly recommended to use electronic notebooks and/or logbooks for recording information on a research project. This presents a number of benefits, such as efficient organisation, searchability, enhanced accessibility, collaboration, and integration across systems. GSI/FAIR offers a number of tools to support this.
For experimental logging and project documentation, the Electronic LOGbook (ELOG)) is available. Further information can be found here. In addition, an active Mattermost channel is available (internal only) to discuss issues, suggestions and provide support.
For managing tasks, documentation, and project information distribution, wiki services are available.
For version control, collaboration, and project issue tracking a GitLab hosted by GSI/FAIR is offered.
Creating a record with a persistent identifier (such as a DOI) and accompanying documentation for research infrastructure (e.g., experimental instruments) serves to ensure long-term availability and citability of device information. Generating these records offers numerous benefits, including:
- Informing users: Records serve as reference points, providing insights into technical specifications and aiding device discoverability.
- Providing traceability: Ensures devices are traceable and distinguishable for effective monitoring.
- Direct citation: Acting as a reference point for instruments, updatable as needed, without replacing technical articles.
- Version control: Keeps updates and modifications reported.
- Long-term accessibility and knowledge retention: records with a persistent identifier ensure information related to the instrument remains accessible over time.
An example can be found in the GSI Publications Repository here.
A template for the documentation can be accessed here.
For instrument publication inquiries, please contact us for further details and steps.
Contact persons for each project can be provided upon request. Please contact open-science(at)gsi.de
GSI membership in Open Science Associations
Open Science oriented projects
- ESCAPE (EOSC)
- PUNCH4NFDI (NFDI)
- OpenTransfer Project
- Helmholtz Matter & Technology, Data Management and Analysis (MT-DMA)
- Helmholtz MetaData Collaboration
- JOIN2
Other projects with OpenScience aspects/applications
Events:
The 1st Open Science workshop at GSI/FAIR was held on 19th and 20th October 2023, taking place over two afternoons 13:00-17:00. Within an open and informal environment, the workshop focused on various Open Science Themes related to GSI and FAIR. This included Open Access publications, Research Data Management, and Open Source Software, Open infrastructure, and GSI/FAIR participation in external Open Science Projects.
Slides and information can be found here.
Online training materials:
- PhD Passport for Open Science
- FOSTER - Open Science Training Courses
- Open Science MOOC
- Open science trainer’s corner
- Forschungsdatenmanagement - Eine Online-Einführung (in German only)